Proprietary Technologies For Drug Products
Particle Sciences employs a wide range of non-proprietary technologies to tackle clients’ bioavailability and formulation challenges. At times, clients may be looking to utilize a patented technology as part of their intellectual property strategy or they may face a problem that needs a specialized technique. In these cases, Particle Sciences offers several proprietary technologies that may meet clients’ commercial and technical needs.
SteriMill™ Nanomilling
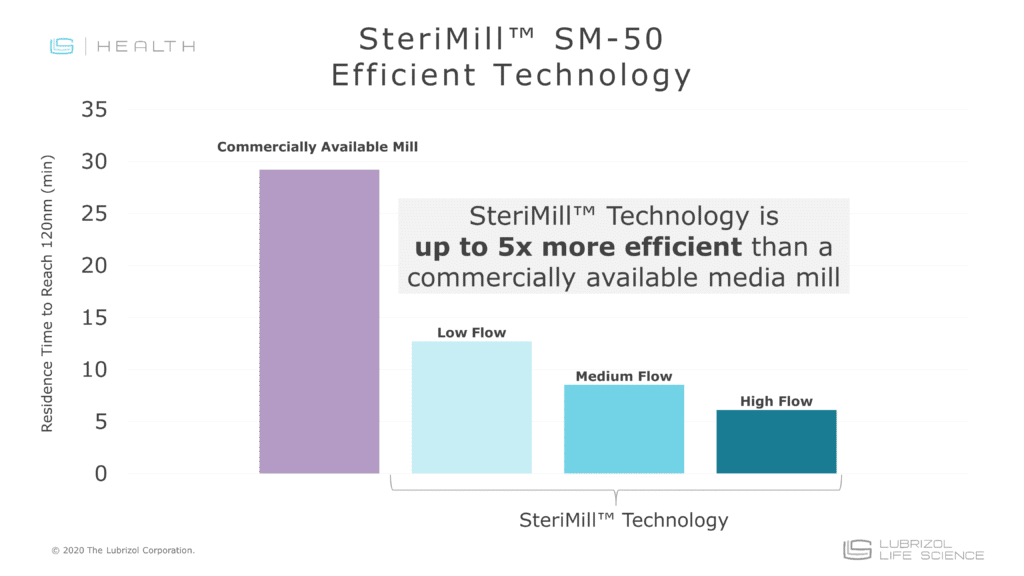
Particle Sciences’s proprietary SteriMill™ nanomilling technology employs high energy media milling (AKA nanomilling) to reduce particle size and increase the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble APIs. The technology uses custom miilling equipment that enables aseptic production of nanosuspensions from R&D through commercial scale—a benefit that cannot be achieved with traditional mills.
Nanomilling is a nearly-universal, top-down approach to solubility enhancement with several benefits, including:
- NO harsh organic solvents or pH extremes: Most nanomilled suspensions are aqueous-based
- High API concentrations: 5-40+% API (w/w)
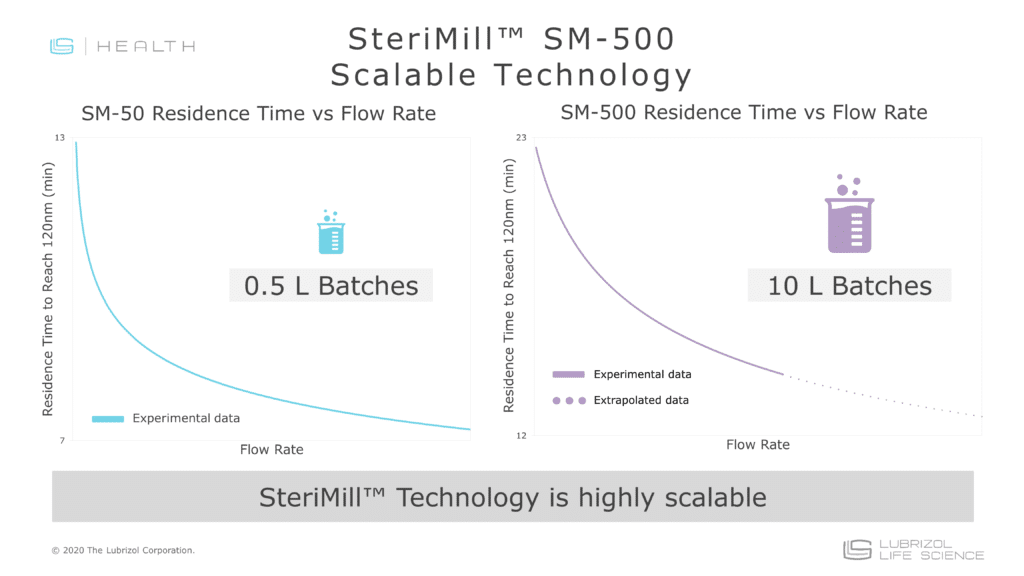
- Easy Scale-Up: Nanomilling utilizes a recirculation process that allows batch sizes to increase without changing process variables
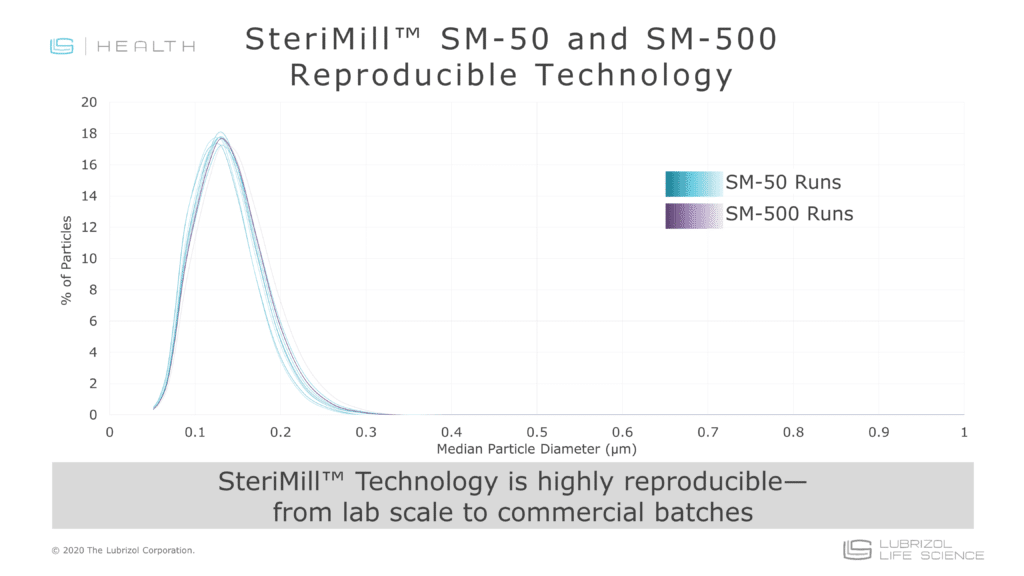
- Reproducibility: Once a nanomilling process is optimized, there is minimal variation in particle size from batch-to-batch
The technology behind nanomilling was developed in the 1980s and the first FDA-approved nanocrystal drug came to market in 2000. Since then, numerous BCS class II and IV APIs have benefitted from nanomilling and gained FDA approval. Nanomilling has been used to increase bioavailability and minimize fed/fasted variability in both liquid and solid dosage forms.
SATx™ Technology
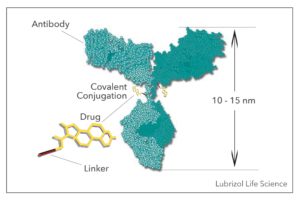
Our Surface Arrayed Therapeutics (SATx™) technology offers a simpler, more versatile approach to “linking” a biological molecule with an API compared to more traditional methods such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). ADCs involve covalently attaching an antibody to a drug molecule, which alters the molecule. The new molecular entity (NME) created requires extensive characterization, accompanied by increased regulatory challenges that are associated with a NME. With SATx technology, a drug is encapsulated in a lipid nano- or micro-particle using a straightforward process. When an antibody or other biological molecule is attached to the particle, it is done so electrostatically, so no conjugation chemistry is involved, and the drug is unaltered.
While both SATx technology and ADCs offer the ability to target tissue in the body with high specificity, only SATx technology can handle dramatically higher drug loading. This technology can deliver a broader range of pharmaceuticals than typical ADCs, allowing for greater formulation flexibility, and the minute particle size evades rapid clearance from the body.